 |
| Big Data is one of the 4 technologies (Mobile, Cloud, Social and Big Data) that make up 3rd Platform. |
Big Data is defined as any data that cannot be handled using traditional IT methods
 |
| Big Data Challenges |
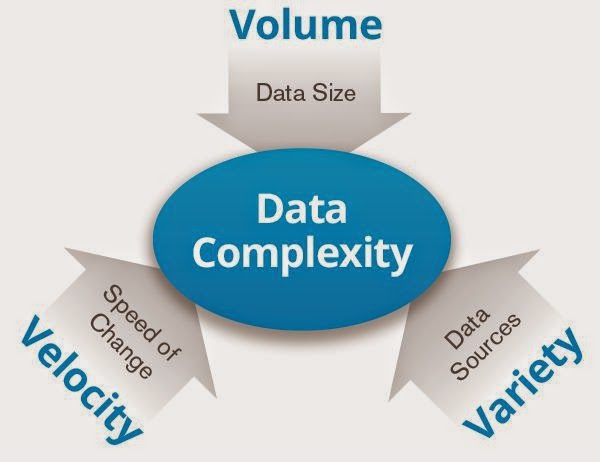
Calling it BIG data makes people only think that it's about the VOLUME of data but Big Data encompasses fast velocity data as well as varied types of data.
 |
| 3 Vs |
Volume
Velocity
Variety
Volume:
Data, free to create, NOT to store. IT has been storing digital data for 50+ years. As the cost of data storage devices decrease, the trend toward retaining low value data has been on the rise. After all there is value in ALL data if you just find a way to extract it. While it's hard to store 100 million pennies, if you find a way to cash them in... it's still 1 million bucks. The trick is finding a low cost method to store, manage and extract value from the data.
Hard drive capacities have increased making it easier to store large amounts of data on fewer drives. The cost however is not simply the device to store the data on but from managing the data. Large volumes of low value data require you need to leverage technologies like...
 |
| Data Compression |
Compression - a method of storing the same amount of information in less space. Not all data is compressible. Media files like pictures and video are already compressed and cannot be stored in a smaller size. Encrypted data is not compressible.
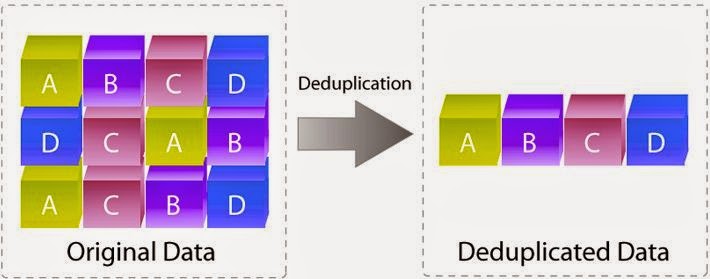 |
| Data Deduplication |
Deduplication - never store the same data twice. Save cost and simply recreate the original data from the data you stored.
 |
| Scalability |
Scalable Data Containers - storage container size can simply grow to accommodate data growth. Can your data container grow as your data volume does? Individual storage device limits force the use of many storage devices and drives up complexity and costs.
 |
| Data Protection Methods |
Efficient Data Protection Methods - creating a separate copy of each piece of data to plan for a device failure will force you to have 2X the amount of storage capacity. Your Big Data problem just doubled. You need more efficient data protection algorithms.
 |
| Power Costs |
Power & Cooling Costs - storage devices must reduce the amount of power they consume or you will pay more money to power and cool your data then the value it has locked inside it.
Variety:
Applications are the automation of business processes. Those processes (applications) create data. Business apps such as ERP, CRM and sales ordering applications create data using input forms whose fields that fit perfectly into the tables of a database. These applications don't just store their data but frequently search that data and rely on the relational database to perform fast searches. The applications make requests to the relational database via SQL statements and the database returns a set of records (recordset) that matches the SQL query statement. To summarize, the structure of the backend database conforms to what is mandated by the forms users use to enter the data in the applications.
Not all Apps are HUMAN
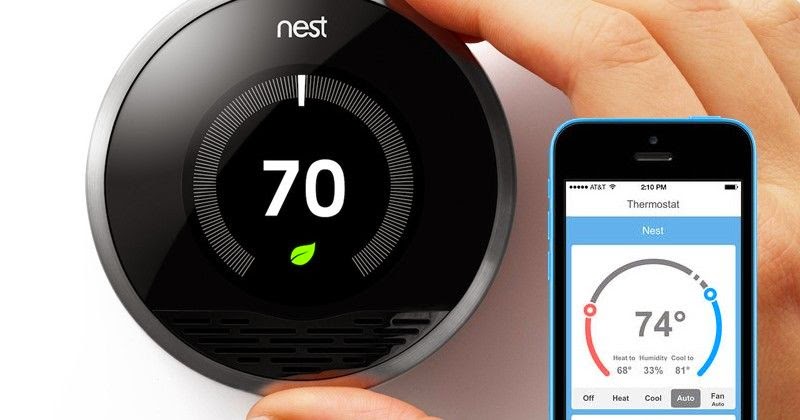 |
| Nest Home Thermostat |
Not all applications enter their data using nice form fields that fit perfectly into a database table. Heck, some applications are not even humans creating the data. Examples would include a Nest home automation thermostats (just acquired by Google for $3.2B). Not all applications need a DB to constantly search, aggregate and display data that they have previously saved. An example would be an CRM app that lists all a customers previous orders.
Unlock the Value Hidden in Big Data
 |
| Unlocking Information Hidden in Data |
Herein lies the problem. These new devices and applications don't use a database but instead simple files to store their data. Businesses typically collect all their DB data into a data warehouse (large collection of DB data) for analysis and reporting. The DW (data warehouse) reports will track KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that help leaders make business decisions. Business leaders must make decisions everyday. Those with the most information make the best decisions. That information is hidden in the data and must be extracted with analysis. What about all the varieties of data that don't fit in a database and ultimately make it into your data warehouse for analysis? You are leaving lots of valuable data and the information it would give you hidden in those files. Big data is about getting access to that information to make your business more competitive, productive and profitable.
 |
| Business Justification to Drill |
Tapping into big data is like drilling for oil. When the oil first comes out of the ground it takes a small amount of effort and money making it profitable to go after. When oil extraction and refinement costs are more than the price we can get for oil on the open market there is no business justification to extract it. The oil, just like the big data in files will remain there until the value goes up or a cheaper way to extract the oil (information) is created.
Let the Drilling Begin!
Enter FREE open source NoSQL databases and cost efficient scale-out block & file systems running on commodity hardware. Suddenly, the cost to extract the data has come way down.
Enter Social Media and its hugely valuable customer preference data.
Suddenly there is a business justification to go after the information locked in these unstructured files.
Social Networking and the internet have created many new data sets or streams that are unstructured data (not structured like in a database). If you want to analyze this type of data you will need something different than a relational database. Recent advances in non-relational databases have given IT shops the ability to easily analyze unstructured or semi-structured data.
What is a relational database? A relational database is a collection of related tables of data. These tables are under the control of the RDBMS - Relational DataBase Management System. The RDBMS is the database application where the database is the collection of related tables of data.
Velocity:
 |
| How Many Tweeters? |
Human beings can create data via typing at say 60 words a minute. A million Twitter users can create data at 60 million words a minute. Velocity is trying to consume all the Twitter tweets of millions of people in real-time.
 |
| IoT - Internet of Things |
Humans are not the only ones creating the data. Smart machines are now sending their data over the internet. We call this concept the IoT or Internet of Things. Gone are the days of calling your customer to ask how they are using your products. Smart companies are embedding simple inexpensive internet hardware into their products that stream useful information home to product teams. How could your company benefit from this type of data? Extracting value from this data often requires that you can analyze it in real-time. This data is not structured so you can't wait to modify it to fit into your database or a data warehouse. Even writing the data to disk and attempting to read it back for analysis may simply be too slow. New methods of using large amounts of RAM to store and query the data for analysis have appeared.
 |
| Stream Analysis |
Your business's competition is building IT solutions to retrieve these fast data streams and analyze them in real-time to make better decisions about how to interact with their customers. Companies that can innovate the fastest by leveraging technology win.
Conclusion:
The era of Big Data is here. Companies large and small are being disrupted by their competition who are leveraging Big Data. There are examples everywhere of how to use Big Data. There is a learning curve to dealing with big data and it's one you will want to get ahead or you may be finding yourself chasing your competition.






















